Exchange Online & Mail Security – Training
| Description | MS-EXO1 & MS-EXO2 (WEY-EXO) |
| Author(s) | Stefan Wey |
| Copyright | Copyright © 2024 Stefan Wey |
Home («MEXO1»)
Welcome to the Exchange Online & Mail Security – Essentials Training («MEXO1») course!
This training is designed to equip you with the essential skills and knowledge required to manage and secure Exchange Online.
Key Learnings
- Implementing and managing Exchange Online: Malware protection, spam blocking
- Email flow management: routing rules, connector configuration
- Optimizing message security: phishing, quarantine
- User and group management: delegated administration, user experience optimization
Resources
- Note: "Exchange Hybrid and Entra Connect (Identity Sync)" is not included in this course
- Note: "Outlook and Microsoft 365 Apps (Office)" is not included in this course
Appendix
Labs
Path 1 & 2
Path 3 & 4
Modules
Path 1
Mail (Exchange Online)
Basic Introduction
Admin Portals
| Name | Url |
|---|---|
| Microsoft 365 Admin Center [MAC] | https://admin.cloud.microsoft (New) |
| Microsoft 365 Admin Center | https://admin.microsoft.com (Classic) |
| Microsoft 365 Admin Center | https://aka.ms/admincenter |
| Exchange Admin Center [EAC] | https://admin.cloud.microsoft/exchange (New) |
| Exchange Admin Center | https://admin.exchange.microsoft.com (Classic) |
| Microsoft 365 Defender [MDO] | https://defender.microsoft.com |
| Microsoft 365 Defender (Microsoft 365 security) | https://security.microsoft.com (Classic) |
| Microsoft 365 Defender | https://aka.ms/de |
| Microsoft Purview | https://purview.microsoft.com (New) |
| Microsoft Purview (Microsoft 365 Compliance) | https://compliance.microsoft.com (Classic) |
Exchange Licensing
| Name | MailboxSize | Features | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Online (Plan 1) | 50 GB | Email hosting, web-based access, calendar, and contact management | $4.00 / CHF 3.60 User/Month |
| Exchange Online (Plan 2) | 100 GB | All features of Plan 1 + DLP (Data Loss Prevention), in-place hold | $8.00 / CHF 7.20 User/Month |
| Exchange Online Archiving for Exchange Online | N/A | Unlimited archiving, in-place archive, retention policies | $3.00 / CHF 2.70 User/Month |
| Exchange Online Protection (EOP) | N/A | Anti-spam and anti-malware filtering for inbound and outbound emails | Mostly included or $1.00 / CHF 0.90 User/Month |
| Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (Plan 1) | N/A | Protection from malware (Safe Attachments), phishing (Safe Links), and spoofing | $2.00 / CHF 1.79 User/Month |
| Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (Plan 2) | N/A | All features of Plan 1 + investigation and response capabilities | $5.00 / CHF 4.50 User/Month |
- https://m365maps.com/
- Compare Exchange Online plans
- Exchange Online service description
- Exchange Online Protection
- Exchange Online Protection service description
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365 service description
- Exchange Online Archiving
- Exchange Online Archiving service description
- Microsoft Purview service description
Recipient Management
UserMailbox vs SharedMailbox
| Feature | User Mailbox | Shared Mailbox |
|---|---|---|
| License | Requires a Microsoft 365 license | No license needed (if under 50GB storage) |
| Login | Can be accessed with a username/password | Cannot be logged into directly; accessed via delegation |
Mailbox Settings
Mailbox settings offer a suite of functionalities for personalized and efficient email management. Users can easily update their display names, enhancing personalization and branding. Alias options provide additional flexibility in email address usage. Automatic replies streamline communication by informing contacts of user availability. Quotas ensure effective storage management.
- Mutation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
Mailbox Permissions
In Microsoft 365 (Office 365), mailbox permissions allow administrators to manage access to user mailboxes. Different types of permissions include:
- SendAs Permissions: Allows a user to send emails as another user.
- Send-on-behalf Permissions: Enables sending emails on behalf of another user.
- Full Mailbox Access: Grants access to a user's entire mailbox.
- Delegate (Deputy) Access: Designates a deputy to manage a mailbox in the owner's absence.
1 2 3 | |
Automapping
- Add Permission over Admin Center
- Automapping: On by
Default
- Automapping: On by
- Add Permission over PowerShell
- Automapping: On (or Off with
Attribute)
- Automapping: On (or Off with
| Option | Client | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Automapping: On | Classic Outlook (for User) | Mailbox will be added |
| Automapping: On | Classic Outlook (with Group) | No automatic action |
| Automapping: Off | Classic Outlook + Add Additional Mailbox | Manual add needed (Legacy) |
| Automapping: Off | Classic Outlook + Add Account | Alternative (Auto-Signature) |
| Automapping: On | Outlook Web | No automatic action |
| Automapping: On | New Outlook | No automatic action |
| Automapping: On | Outlook App | No automatic action |
| N/A | Outlook Web + Add Shared Mailbox (On Inbox-Folder) | Manual (Modern) |
| N/A | Outlook Web + Open Mailbox (Right-Top) | Outlook SendAs ignored (Legacy) |
| N/A | New Outlook + Add Shared Mailbox (Inbox) | Without Calendar (Missing) |
1 | |
Calendar Permission
General Knowledge: Calendar permissions in Microsoft 365 (Office 365) allow administrators to control who can access a user's calendar. Different permission levels include:
- Read-only: Users can view calendar events but cannot make changes (limited details).
- Reviewer: Users can view calendar details but have no editing permissions (including extended event information).
- Editor: Users can view and modify calendar events.
- Owner: Full control over the calendar, including adding or deleting events.
Add Mailbox Permission for Calendar
1 2 | |
Change Mailbox Permission for Calendar
1 2 | |
Calendar Processing
General Knowledge: Calendar processing automates tasks related to meeting management. Key features include:
- Booking Meetings: Automatically accept or decline meeting requests based on availability.
- Handling Meeting Requests: Automatically process meeting invitations and send responses.
- Resource Calendars: Manage shared resources like meeting rooms or projectors.
1 2 3 4 | |
Shared Mailbox Settings
If a shared mailbox is set up and automatically added using Auto Mapping in Outlook, due to the Full Access authorization, the sent e-mail will not be found under sent items of the shared mailbox when sending an e-mail. Accordingly, the following should be configured to prevent this problem:
Automatically save sent items in delegator's mailbox in Exchange Online
1 | |
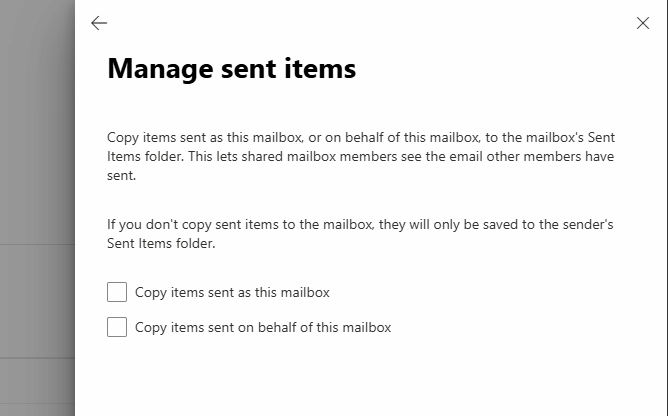
Items that are deleted from a shared mailbox go to the wrong folder in Outlook
1 2 3 | |
Permission (Admin roles)
Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
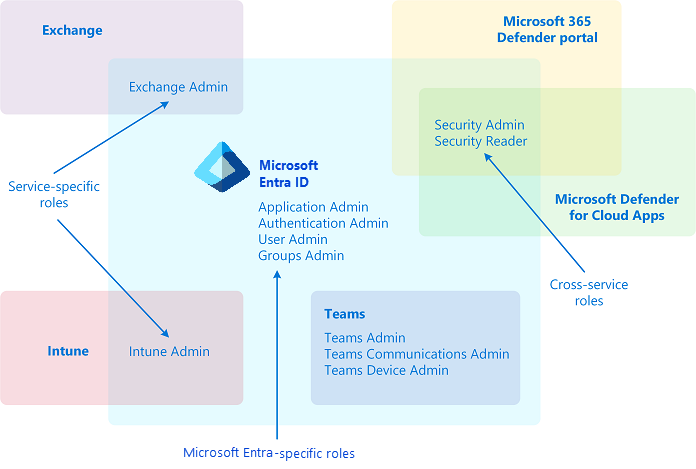
Entra ID Roles
Entra roles in Entra ID (Azure AD) are pivotal for managing permissions and access within an organization. Role Assignments allow administrators to allocate roles to users, groups, or service principals, defining their permissions. Privileged Identity Management (PIM) enhances security by enabling just-in-time role activation, requiring approval for role activations, and enforcing multifactor authentication. PIM also provides time-bound access with automatic deactivation, ensuring that elevated permissions are temporary and used only when necessary.
Type:
- Global roles with [high usage]
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Global Administrator | Can manage all aspects of Microsoft Entra ID and Microsoft services that use Microsoft Entra identities. |
| Exchange Administrator | Can manage all aspects of the Exchange product. |
| Exchange Recipient Administrator | Can create or update Exchange Online recipients within the Exchange Online organization. |
| Password Administrator | Can reset passwords for non-administrators and Password Administrators. |
Exchange Online Roles
Exchange Online roles determine permissions for managing various aspects of the service. The major roles include the Organization Management role, which grants full access to administrative features, and the Recipient Management role, for managing recipients. Other roles, like Compliance Management and View-Only Organization Management, provide more specific access, such as overseeing compliance or granting read-only access to organizational data.
The role Mailbox Import Export allows users to import and export mailbox data, enabling the transfer of email content to and from mailboxes within Exchange Online.
Types:
- Administrative roles with [indirect/medium usage]
- End-user roles with [low usage]
| Entra ID or Microsoft 365 role | Exchange Online role group |
|---|---|
| Global administrator | Organization Management, Recipient Management, Compliance Management, View-Only Organization Management |
| Global Reader | View-Only Organization Management |
| Exchange Administrator | Organization Management |
| Exchange Recipient Administrator | Recipient Management |
| Helpdesk Administrator | Help Desk administrator |
| Password administrator | No direct equivalent Exchange role |
Protection - Part 1 (Basic)
DKIM / Email authentication
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): DKIM is a method of email authentication that helps validate mail sent from your Microsoft 365 organization. It prevents spoofed senders commonly used in business email compromise (BEC), ransomware, and other phishing attacks. By digitally signing outgoing emails, DKIM ensures their integrity and authenticity.
- Digital Signature: DKIM generates a unique digital signature using a private key and attaches it to the email header.
- Verification: The recipient's mail server retrieves the sender's public key from the DNS and verifies the digital signature to confirm the email's authenticity and integrity.
- Implementation: Domain owners generate cryptographic keys, configure mail servers to sign emails with the private key, and publish the public key in DNS records as a TXT entry.
| Setup Option | DNS Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| delegate | CNAME | Delegated Control, Simplified rollover (Not automated yet) |
| direct | TXT | Self Controlled, Manual rollover |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
Reference:
Phishing (Policy, SPF) / Anti-phishing
Sender Policy Framework (SPF): SPF identifies valid email sources for your Microsoft 365 domain. It confirms that the domains in the MAIL FROM and From addresses align and that the message comes from a valid source for the From domain. DMARC uses SPF results to verify alignment between these domains, eliminating ambiguity between hard fail (-all) and soft fail (~all) results.
| Name | Qualifier (Prefix,Ending) | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| softfail | ~all | A "softfail" result ought to be treated as somewhere between "fail" and "neutral"/"none". The ADministrative Management Domains (ADMDs) believes the host is not authorized but is not willing to make a strong policy statement. | spam or suspicious (possible DKIM) |
| fail (hardfail) | -all | A "fail" result is an explicit statement that the client is not authorized to use the domain in the given identity. | rejected/discarded |
| neutral (none) | ?all | A "neutral" result indicates that although a policy for the identity was discovered, there is no definite assertion (positive or negative) about the client. | accept/ignored (possible DKIM) |
| pass | +all | A "pass" result means the client is authorized to inject mail with the given identity. | accept (default prefix) |
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
Reference:
- Set up SPF to identify valid email sources for your Microsoft 365 domain
- 3rd Parties SPF (https://mxtoolbox.com/spf.aspx, https://dmarcian.com/spf-survey/, https://easydmarc.com/tools/spf-record-raw-check-validate, https://easydmarc.com/tools/spf-lookup)
- Note: "Impersonation settings" are not included in this article
Spam filter / Anti-spam
A spam filter, or anti-spam filter, is a software solution that uses algorithms to identify and block unwanted emails. These algorithms analyze email attributes such as content, sender reputation, and patterns to distinguish spam from legitimate messages. Effective spam filters ensure a cleaner, more organized inbox, enhancing email efficiency and productivity.
- Inbound spam:
- Bulk email threshold (High or Low)
- Spam vs High confidence spam (Junk or Quarantine)
- Allowed senders / Allowed sender domains (use "Tenant Allow/Block List")
- (SPF record: hard fail)
- (Sender ID filtering hard fail)
- (Backscatter)
Reference:
Malware filter / Anti-malware
A malware filter, or anti-malware filter, is a security tool designed to detect and block malicious software. By using advanced algorithms and real-time scanning, it identifies and neutralizes threats such as viruses, worms, and trojans. This ensures the protection of systems and data, maintaining the integrity and performance of devices.
- Zero-hour Auto Purge (ZAP) ~ Automatic cleanup
- Common attachments filter (FileType)
Reference:
- Anti-spam, anti-malware, and anti-phishing protection in EOP
- Zero-hour auto purge (ZAP) in Microsoft Defender for Office 365
Setup Quarantine
Quarantine and Quarantine Notifications: Quarantine holds potentially dangerous or unwanted messages in Microsoft 365 organizations with mailboxes in Exchange Online or standalone Exchange Online Protection (EOP) organizations. Quarantine notifications allow users to release and report quarantined messages. Admins can customize notification settings, including sender information, logo, and frequency:
Reference:
- Quarantine (End-User): https://security.microsoft.com/quarantine
- Anatomy of a quarantine policy
- Use quarantine notifications to release and report quarantined messages
Quarantine Policy
The Quarantine Policy allows administrators to manage and review suspicious emails, ensuring they don't reach users' inboxes, enhancing security and control over potential threats
Definition:
| Types | Default Policy | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| No access | AdminOnlyAccessPolicy | No Release |
| Limited access | N/A | Request Release > System alerts for quarantine release requests |
| Full access | DefaultFullAccess*Policy, NotificationEnabledPolicy | Self-Release (apart from Malware) |
Assignment:
- Files Types & Malware > EOP anti-malware policy settings
- Spam & Phishing > EOP anti-spam policy settings
- Spoofing & DMARC > EOP anti-phishing policy settings
Quarantine Notifications Policy
The Quarantine Notifications Policy allows administrators to notify users about quarantined messages, ensuring timely review and action on potential threats
- Notification frequency (every four hours, daily, or weekly).
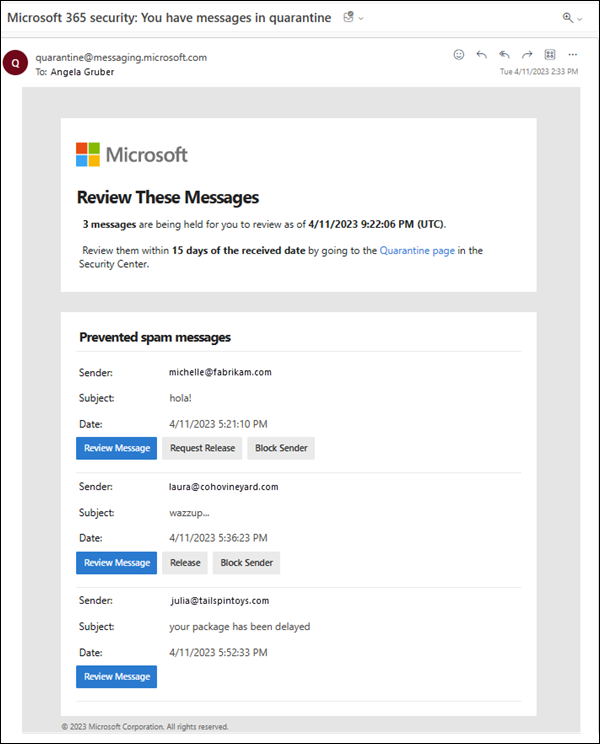
Mail flow
Manage mail flow: Managing mail flow for Exchange Online is the easiest way of configuring mail flow because it's all configured by default and managed by Microsoft. As such, mail flow in Exchange Online is considered a 'black box' because mail flow is handled internally within Exchange Online with no assistance from Exchange Administrators. While administrators can create other connectors to improve the organization's mail flow, they have no other impact on the mail flow process.
- Accepted domains (Authoritative domains, Relay domains), Remote domains
- Connectors (Inbound Connectors, Outbound Connectors)
Troubleshoot mail flow:
- (Read NDR/DSN messages carefully, twice): NDR or SMTP errors
- DSN: Delivery status notifications
- NDR: Non-delivery reports
- Verify mentioned message in "Message trace": Exchange Admin Center > Mail flow > Message trace
- Ask how many users are affected (single user or multiple users)
- Request or Find Msg-File (Message Header)
- Verify MX Records (DNS Entry): https://mxtoolbox.com/MXLookup.aspx > Domain Name
- Verify Connection: https://testconnectivity.microsoft.com > Inbound SMTP Email
- Inbound Confirmed:
- Check Exchange Rules (Mail Flow Rules, Transport Rules),
- Email Forwarding or Redirection
- Review your configuration (Anti-Spam and Anti-Malware Policies, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC)
- Inbound Missing: Check Microsoft 365 Admin Center > Health > Service Health
- Consider a Possible Escalation to Microsoft Support or IT Consultant
Message trace
The Exchange admin center (EAC) in Microsoft 365 has a Message Trace feature. It helps you track emails as they move through your organization, showing if they were received, rejected, deferred, or delivered. This is helpful for troubleshooting email problems, checking policy changes, and answering questions about message status.
- For 10 days within a 90-day window (Response Time: Instant): Quickly retrieve message traces
- Up to 90 days (Response Time: May take a few minutes to generate): Ideal for detailed investigations
Domains (SMTP domains)
Exchange uses SMTP to send and receive messages between transport services within the same server or across Mailbox servers. Exchange supports two types of SMTP domains: accepted and remote domains. Accepted domains handle email within the organization Remote domains define settings for delivering messages to external domains and include options for message formatting, auto-replies, and non-delivery reports.
Domain Mail Flow Routing:
| Accepted domains types | Description | Exchange Online supported | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authoritative | Where all recipients are hosted internally | Yes (default) | Cloud only, or every recipient is synced |
| Internal relay | Shared between Exchange and external systems | Yes | Hybrid |
| External relay | Processed but not hosted internally | No | Tenant Domain Sharing 1 |
| [Not added] | Not configured, message is rejected | N/A | Sent to unconfigured Tenant |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
Rules (Mail flow rules, Transport rules)
Mail flow rules (Transport rules) are a powerful configuration tool that enables organizations to control their message flow. For example, it's possible to use mail flow rules for blocking messages that match certain criteria, create CC copies of messages and send them to other recipients, or encrypt messages when they leave your organization or if they're sent to certain recipients.
- Forwarding to 3rd Party Applications: Encryption, Signatures
- Mail flow rules (Transport rules) vs Inbox rules (Mailbox)
- Usage of Rules (Last execution)
- Banner (Disclaimer) vs 'First contact safety tip' (Defender)

1 2 3 4 | |
Reports
Exchange in Microsoft 365 provides detailed email and collaboration reports to monitor mail flow. The Mailflow Status Report tracks Edge protection, while Mail Flow Reports offer insights into Exchange Transport Rules and SMTP AUTH clients. Access these reports to identify potential issues and optimize mail routing-
-
Email & collaboration reports (Defender): https://security.microsoft.com/emailandcollabreport
- Mailflow status report (Edge protection)
-
Mail flow reports (Exchange): https://admin.exchange.microsoft.com/#/reports/mailflowreportsmain
- Exchange Transport Rule report (Usage details)
- SMTP AUTH clients report (Basic Auth vs Modern Auth)
-
Usage reports (M365 Admin Center): https://admin.microsoft.com/#/reportsUsage
Settings (Optional)
Exchange Online offers a range of mail flow settings to manage email behavior. Key features include Plus Addressing for dynamic email routing, sending from aliases, and configuring SMTP Authentication. Additionally, settings for legacy TLS clients and Reply-all Storm Protection help improve email management.
- Mail flow settings: https://admin.exchange.microsoft.com/#/settings
- Plus Addressing in Exchange Online
<local-part>@<domain>vs<local-part>+<tag>@<domain>
- Sending form aliases
- SMTP Authentication
- Opt in to the Exchange Online endpoint for legacy TLS clients using SMTP AUTH
smtp-legacy.office365.comvssmtp.office365.com
- Reply-all Storm Protection
- Message Recall (newer)
- Plus Addressing in Exchange Online
Path 2
Advanced Threats
Safe links
Safe Links is a security feature that protects against malicious URLs. When you click on a link within an article, Safe Links scans it for potential threats. If the link is deemed safe, you'll be directed to the intended webpage. However, if it's identified as harmful, you'll be alerted, preventing any potential security breaches or malware infections.
- Exclude (X-MS-Exchange-Organization-SkipSafeLinksProcessing)
- Rewrite URLs (Do not rewrite the following URLs)
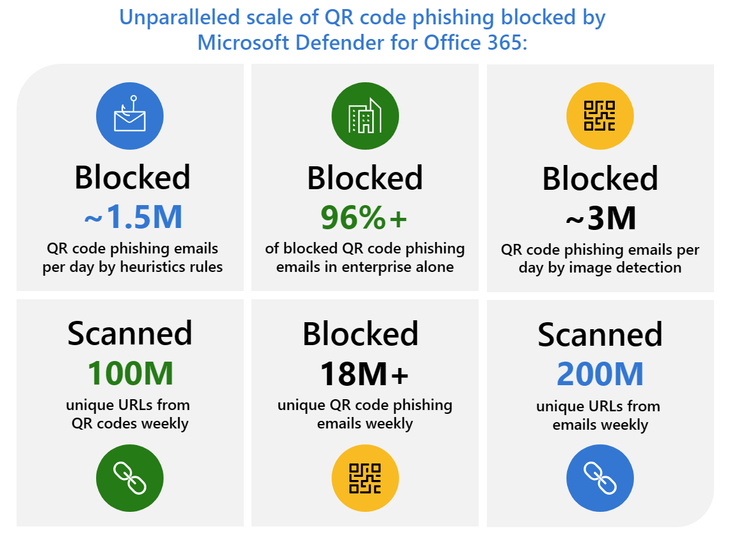
- QR Codes (embedded as inline images within email body, Image Detection > URL Analysis)
Reference:
- Safe Links in Microsoft Defender for Office 365
- Protect your organizations against QR code phishing with Defender for Office 365
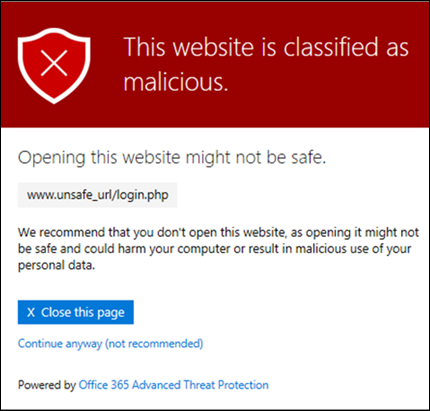
Safe attachments
Safe Attachments is a protective measure that defends against email-based threats. When an email with an attachment arrives, Safe Attachments scans it for malicious content, such as viruses or malware. If the attachment is safe, it's delivered to your inbox as usual. However, if it's flagged as potentially harmful, it's isolated in a sandbox environment for further examination, preventing any damage to your system.
- Exclude (X-MS-Exchange-Organization-SkipSafeAttachmentProcessing)
- Quarantine
Reference:
- Safe Attachments in Microsoft Defender for Office 365
-
Submitting files for malware analysis (Optional)
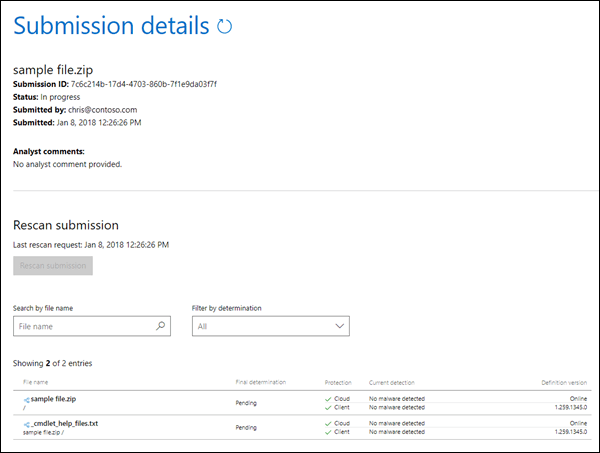
Secure by default (Override)
Secure by Default is part of Microsoft's Secure Future Initiative (SFI), aiming to strengthen security by automatically applying safer settings and limiting overrides that could weaken protection.
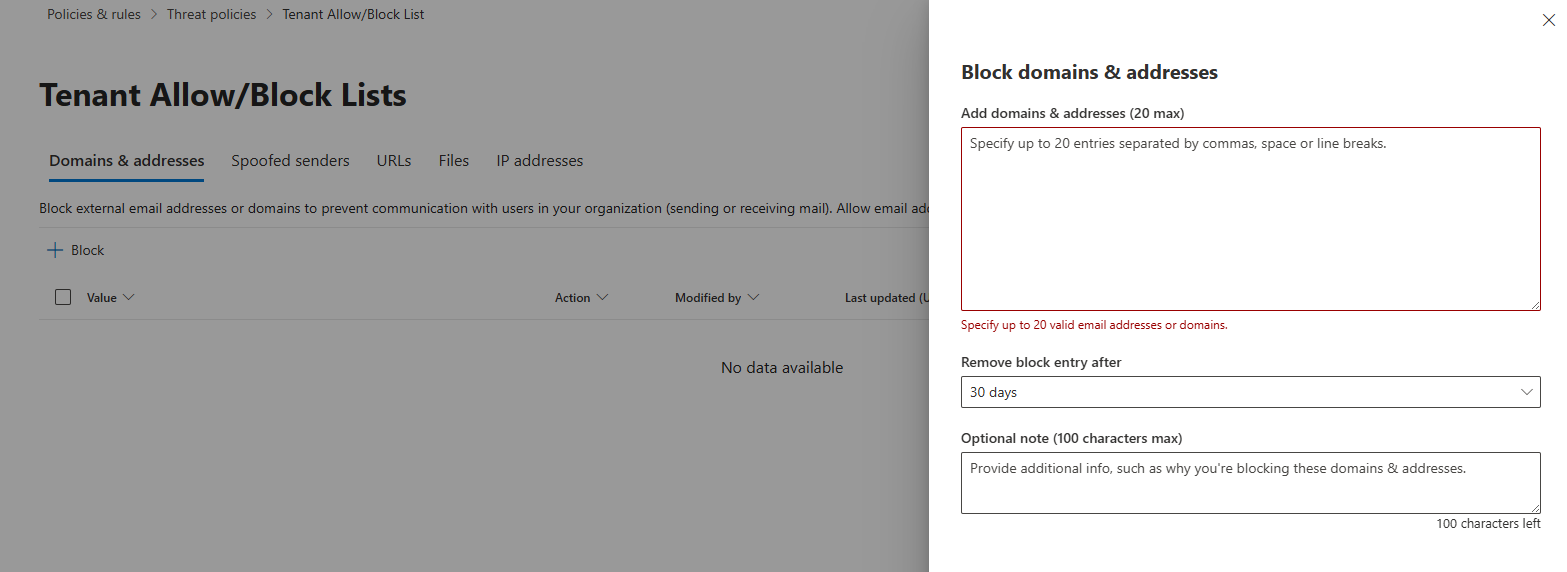
Tenant Allow/Block Lists (Excludes)
The Tenant Allow/Block List allows administrators to manually override filtering verdicts in Microsoft Defender for Office 365 or Exchange Online Protection (EOP). It is used during mail flow for incoming messages from external senders.
Functionality:
- Admins can create and manage entries for domains, email addresses, and URLs.
- The list doesn't apply to internal messages within the organization but can block users from sending email to specific domains and addresses.
You can find the Tenant Allow/Block List in the Microsoft Defender portal under Policies & rules > Threat Policies > Tenant Allow/Block Lists.
Compliance
Retention policies
Exchange Retention policies (MRM, Legacy) vs Microsoft 365 Retention policies vs Mailbox Litigation Hold
Exchange Retention Policies (MRM, Legacy) control data lifecycle in exchange only. Microsoft 365 Retention Policies manage data retention in cloud-based environments (Teams, SharePoint, Exchange), offering more flexibility and scalability. Litigation Hold preserves mailbox content for legal purposes, suspending retention policies and ensuring data integrity during litigation. Each serves distinct needs: Exchange Retention Policies are for exchange only, Microsoft 365 Retention Policies cater to cloud-based environments, while Litigation Hold safeguards data for legal compliance and investigations in both on-premises and cloud environments.
Microsoft 365 Retention policies
Apply Retention policies (MRM, Legacy)
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Enable Litigation Hold
Place a mailbox on Litigation hold
Here are the steps to place a mailbox on Litigation hold using the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Go to the Microsoft 365 admin center and then select Users > Active users
- Select the user that you want to place on Litigation hold
- On the properties flyout page, select the Mail tab, and then under More actions, select Manage litigation hold
1 2 | |
Mailbox Settings
Online Archive (In-Place Archive) , Mailbox auditing, Forwarding
Enable Online Archive
Archive Mailbox (50 GB, 100 GB)
The online archive feature in Office 365 allows users to store older emails and documents in a separate location. Benefits of online archives include:
- Efficient mailbox management by moving older emails out of the primary mailbox.
- Improved performance as large attachments are stored separately.
- Compliance with data retention policies.
1 2 | |
- 2 year move to archive
Enable Forwarding
Mail forwarding in Microsoft's ecosystem offers versatile options for efficient email management. Admins utilize "ForwardingSmtpAddress" in Exchange to centrally manage domain-wide forwarding, optimizing communication flow across the organization. Users can personalize their email experience by setting up "ForwardingAddress" in their mailbox settings, ensuring messages reach them seamlessly wherever they are. Inbox rules automate forwarding based on specific criteria like sender or keywords, enhancing organization and productivity. Exchange rules provide advanced control over email routing, allowing for intricate configurations to meet diverse business needs.
- Configure email forwarding for a mailbox in Exchange Online
-
Control automatic external email forwarding in Microsoft 365
-
ForwardingSmtpAddress = Recipient (Validated, Create a Contact)
- ForwardingAddress = String (No Validation)
- DeliverToMailboxAndForward = Copy to Mailbox (Mailbox Quota)
1 2 3 | |
Verify Auditing (Optional)
Mailbox auditing in Microsoft ensures comprehensive tracking and monitoring of user actions within Exchange Online mailboxes. It records various activities such as message access, folder manipulation, and permission changes, enhancing security and compliance. Admins can review audit logs to identify unauthorized access attempts or policy violations, bolstering data protection measures.
- Manage mailbox auditing
- Increased security visibility through new Standard Logs in Microsoft Purview Audit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | |
Protection - Part 2 (Advanced)
Submission
User & Admin
Admin-Originated Submissions
via Ticket
Admins identify and report messages, attachments, or URLs by selecting "Submit to Microsoft for analysis" from the tabs on the Submissions page. These submissions appear on the corresponding tab (except the User reported tab) and undergo checks such as email authentication, policy hits, payload reputation, and grader analysis.
Admin Submission of User-Reported Messages
via Outlook
When user reporting is enabled, suspicious messages appear on the User reported tab. Admins can submit or resubmit these messages to Microsoft for further evaluation.
- Report Submission: https://security.microsoft.com/reportsubmission
Phishing / Anti-phishing
DMARC Policy (DNS Entry), DMARC Report (E-Mail), DMARC Config (MDO)
DMARC
Domain-based Message Authentication
Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC): DMARC further enhances email security. It validates mail sent from your Microsoft 365 organization, preventing spoofed senders. DMARC combines SPF and DKIM results to determine whether a message passes or fails. Organizations can set DMARC policies to instruct how to handle failed messages (e.g., reject, quarantine, or no instruction). Additionally, DMARC provides aggregate and forensic reports for monitoring and analysis.
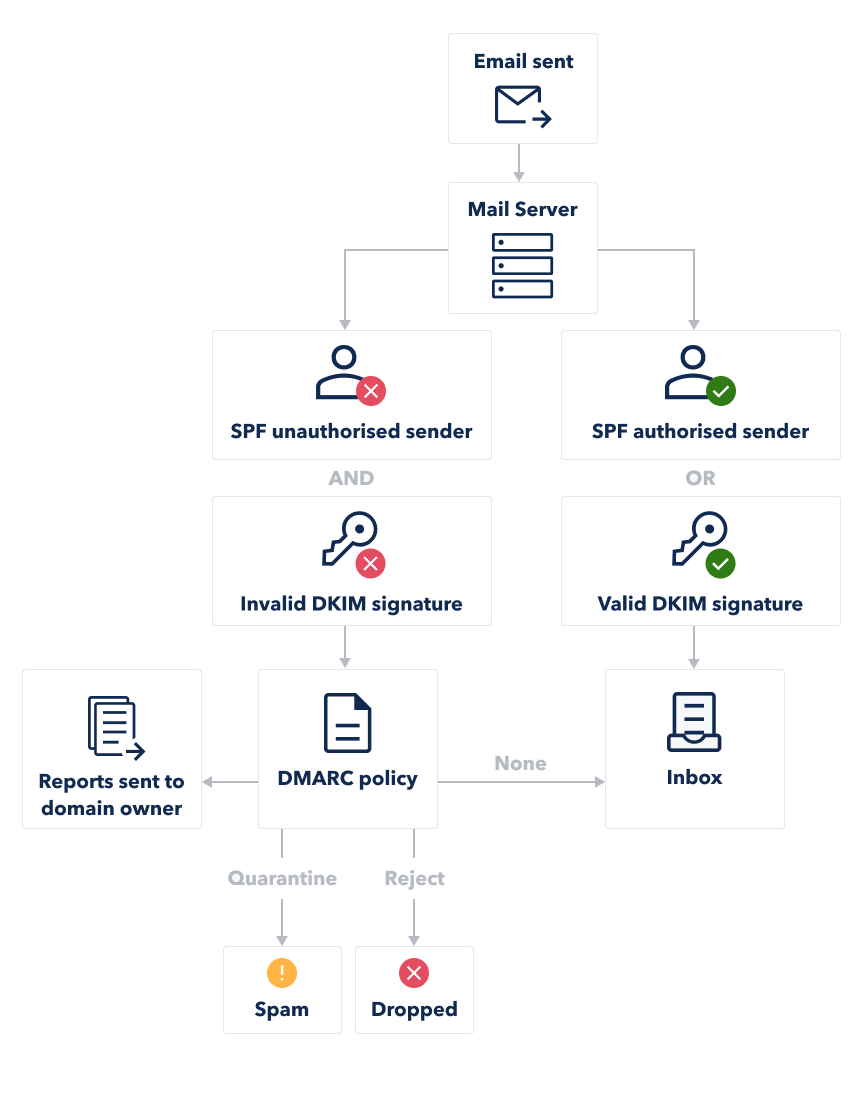
DMARC Policy (DNS Entry)
DMARC Policy (p=none, p=quarantine, p=reject), DNS hosting provider, TXT record
By setting a DMARC policy, domain owners instruct email receivers on how to handle messages that fail authentication checks. This includes reporting, quarantining, or rejecting such emails. DMARC enhances email security by verifying sender authenticity, reducing the risk of domain impersonation.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
| Requested Mail Receiver policy | Description |
|---|---|
| p=none | The Domain Owner requests no specific action be taken regarding delivery of messages. |
| p=quarantine | The Domain Owner wishes to have email that fails the DMARC mechanism check be treated by Mail Receivers as suspicious (considering them to be potentially spam) |
| p=reject | The Domain Owner wishes for Mail Receivers to reject email that fails the DMARC mechanism check |
- Honor DMARC record policy when the message is detected as spoof (EOP anti-phishing policy settings)
Reference:
- Set up DMARC to validate the From address domain for senders in Microsoft 365
- EOP anti-phishing policy settings
- RFC - General Record Format
- How to Publish a DMARC Record
- 3rd Parties DMARC (https://mxtoolbox.com/dmarc.aspx, https://dmarcian.com/dmarc-inspector/, https://easydmarc.com/tools/dmarc-lookup, https://easydmarc.com/tools/dmarc-record-generator)
- DMARC reporting vendors in the MISA Catalog
DMARC Report
Enable Reporting, Analyze Reports
Learn to interpret aggregate and forensic reports, and fine-tune email authentication mechanisms to protect against spoofing and phishing attacks. Gain insights into domain reputation management and improve email deliverability while maintaining robust security measures in Microsoft Exchange Online.
1 2 3 4 | |
- Once (manual)
- XML Analyse Tool 1: https://mxtoolbox.com/dmarcreportanalyzer.aspx
- XML Analyse Tool 2: https://eu.dmarcadvisor.com/dmarc-xml/
- XML Analyse Tool 3: https://easydmarc.com/tools/dmarc-aggregated-reports
- XML Analyse Tool 4: https://us.dmarcian.com/dmarc-xml/
- XML Analyse Tool 5: https://www.zoho.com/toolkit/dmarc-report-analyzer.html
- XML Analyse Tool 6: https://emailconsul.com/dmarcanalyzer
- Periodically (automated report)
- Third-party Tool 1: https://mxtoolbox.com/c/products/deliverycenter
- Third-party Tool 2: https://dmarcadvisor.com/pricing/
- Third-party Tool 3: https://easydmarc.com/pricing/easydmarc/businesses
Phishing policy (DMARC Config)
Microsoft 365 offers built-in anti-phishing features to protect users from various types of phishing attacks, such as impersonation and spoofing. By configuring DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance), organizations can further enhance this protection by verifying the legitimacy of messages.
- Custom Policies: Create rules for specific users, groups, or domains.
- Email Authentication: Use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify emails.
- Phishing Detection: Adjust sensitivity to catch potential phishing attempts.
- Priority Protection: Apply stronger protections for high-risk users.
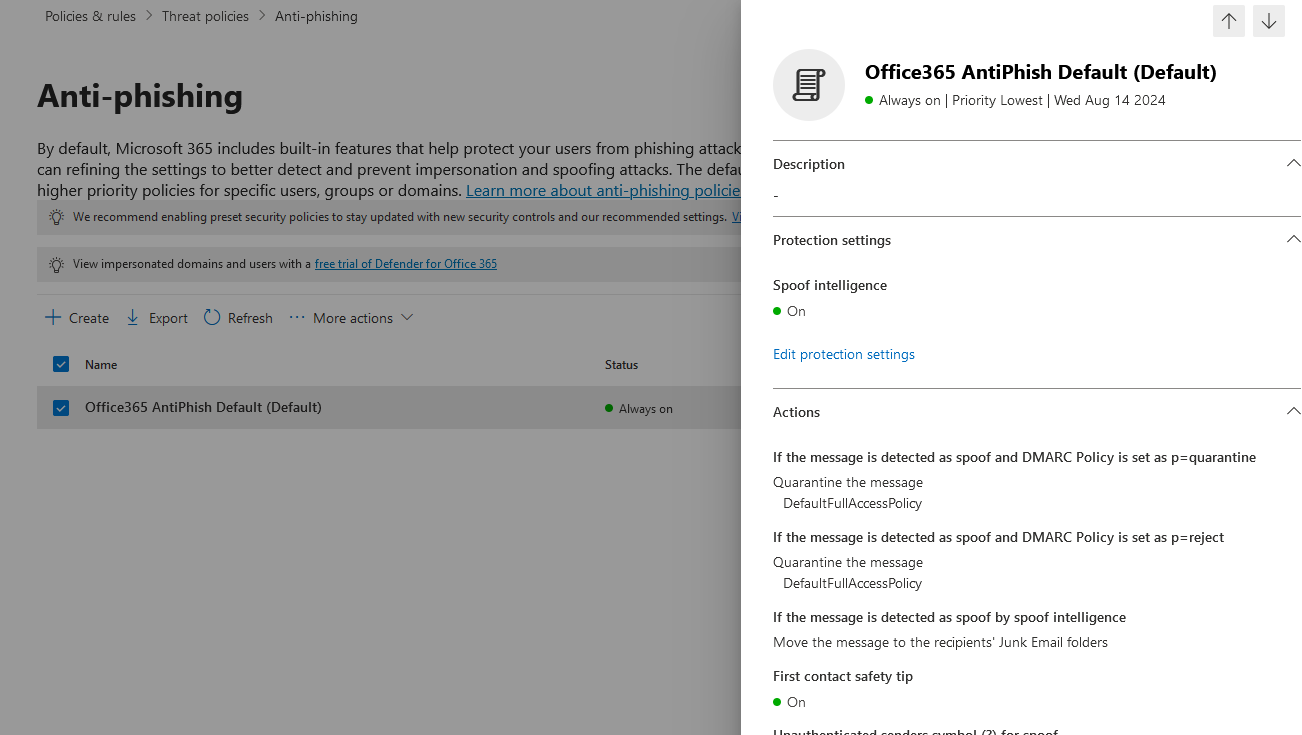
Connection filter (Anti-spam)
Connection Filtering in Exchange Online enhances email security by blocking or allowing messages based on their source. Utilizing IP Allow and IP Block lists, administrators can specify trusted or restricted senders. Moreover, custom allow/block lists enable fine-tuning of filtering rules. By configuring Connection Filtering policies, organizations mitigate risks of spam, phishing, and other email-based threats, fortifying their Exchange Online environment with layered security measures.
- SMTP Relay, 3rd Party Spam-Filter
- Review "Allow Lists" regularly
Others
Sharing (Calendar)
Microsoft Secure Score:
Action: Ensure 'External sharing' of calendars is not available
Description: Users should not be allowed to share the full details of their calendars with external users
- In the Microsoft 365 Exchange admin center, go to Organization > Sharing
- Under Individual Sharing, make sure all policies are unticked (Link)
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
Self-help diagnostics
It's vital that administrators be able to diagnose and resolve issues quickly in Exchange Online and Outlook. To support this effort, the Exchange and Outlook support teams have released some new features in the Microsoft 365 admin center
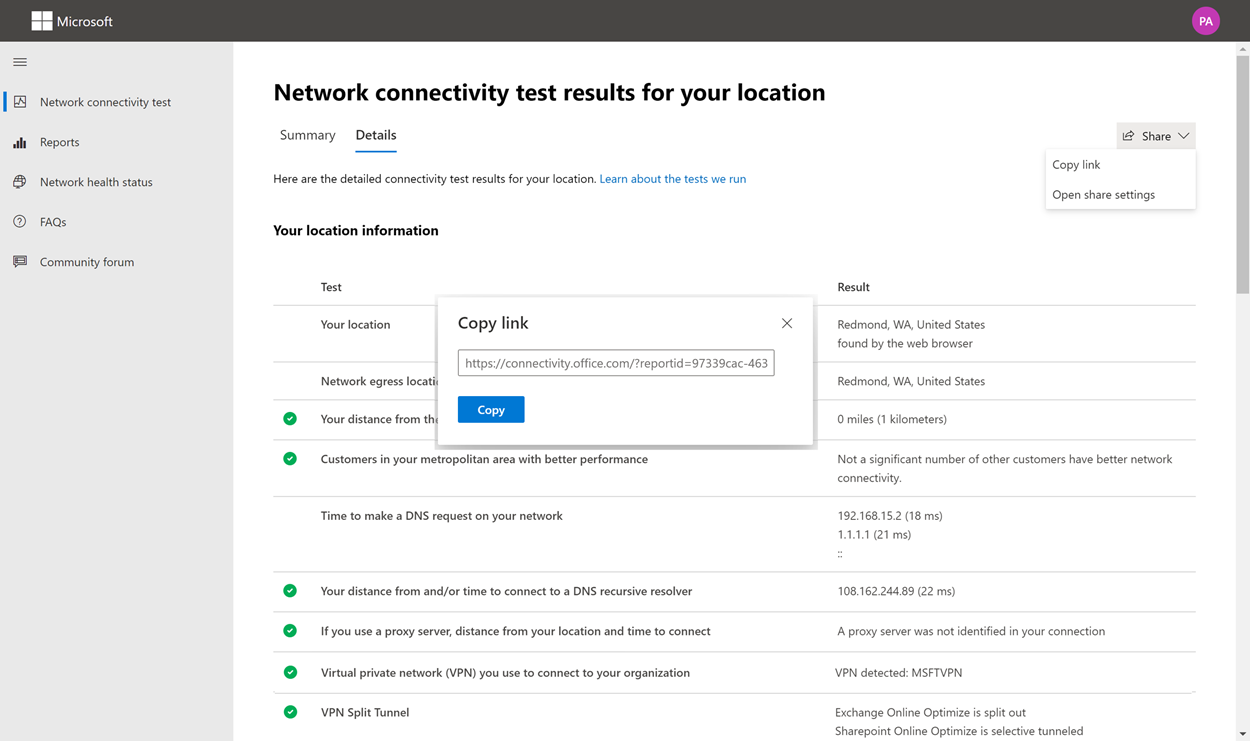
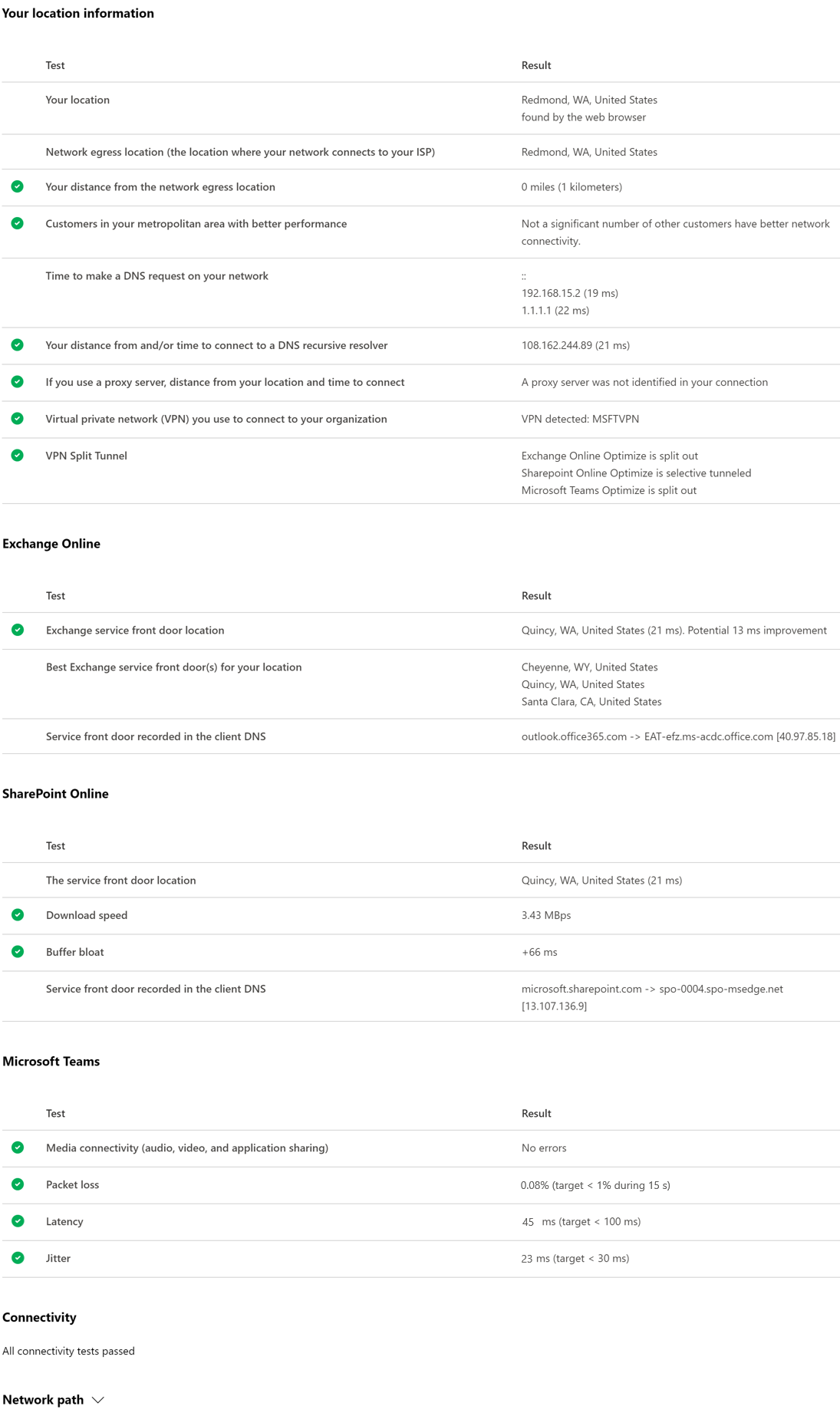
Microsoft 365 network connectivity
- Connectivity test (https://connectivity.office.com/)
- History & traffic (https://admin.microsoft.com/#/networkperformance) > Insights
- Settings > Sharing and user-submitted reports > Allow users to send a link to the report to anyone
Microsoft Secure Score
List of Recommendations:
- Public: Secure Score for EXO & MDO
- Private: https://security.microsoft.com/securescore
Microsoft Remote Connectivity Analyzer
- Function test (https://testconnectivity.microsoft.com/tests/o365)
New Outlook (Classic Outlook)
New Outlook for Windows: A Guide to Product Availability
We will continue to honor published support timelines for existing version of classic Outlook for Windows until at least 2029. Overview of update channels for Microsoft 365 Apps Semi-Annual Enterprise Channel overview
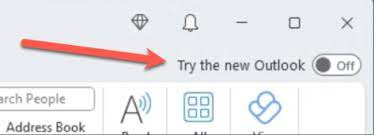
Opt-out
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Time for Feedback
Link: https://learn.digicomp.ch/
Confirmation of participation (Teilnahmenbestätigung) will be available after feedback